Home > Blog > 5 Steps to an Exceptional Product Management Workflow
5 Steps to an Exceptional Product Management Workflow

Product Manager’s responsibilities are vast and complex, with individual tasks varying depending on the organization and the products. But, typically, they are responsible for overseeing the product’s overall success.
For many, this includes numerous tasks, duties, and responsibilities throughout each stage of the product life cycle. As the role can often be demanding and challenging, the manager must remain organized and agile.
This is where an efficient product management workflow becomes key.
What is Product Management?
Product management is the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the life cycle of a product. In most cases, the product manager is typically responsible for developing and executing a product’s strategy and ensuring that the product meets its stated objectives.
The correct execution of this role is critical for the successful delivery of the products because it enables businesses to coordinate and manage the production process from start to finish.
Product managers also help identify and respond to changes in customer demand, while ensuring the correct quantity and quality of products are delivered on time. This lends well to optimizing resources more efficiently.
What are the 5 steps to achieving an exceptional product management workflow?
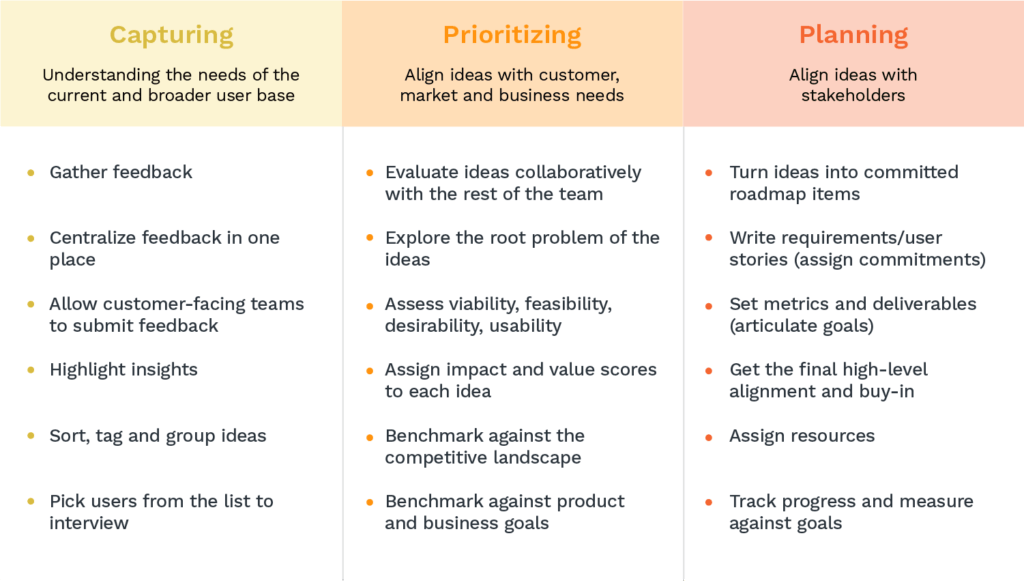
1. Gather your ideas
One of the most important aspects of this role is managing ideas and expectations. They need to identify potential problems and solutions early on in the process, while looking at the bigger picture and understanding how the various ideas fit together.
Not all ideas are created equal. Product managers must select the most promising ideas and discard the ones that are not feasible or will not help the project achieve its goals.
Once the more promising ideas have been selected, the product manager must develop a plan to bring them to fruition. This includes creating a timeline and budget and determining who will be responsible for each task. The product manager oversees the work and makes sure it is proceeding according to plan.
2. Specifications
Project specifications are essential as they are used to set the project strategy and blueprint. The specifications should be used to understand what is needed for the project and to set the expectations for the team.
The project specifications will usually cover the following items:
- The objectives of the project
- What the project scope includes
- The constraints of the project
- Available resources
- The timelines for the project
From here, the data and information can be used to form a clear project plan. This will outline how the project will be completed, what resources are needed, and how to meet the set objectives.
An effective process includes writing user stories to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT). User stories are brief, specific descriptions of how a user would interact with a system or product. They help product managers and team members understand the users’ needs and the feasibility of implementing specific features.
Seamless management platforms like craft.io have intuitive road-mapping capabilities through interfaces designed to communicate your product’s specifications and strategy.
When user stories are used in conjunction with SWOT analysis, the software can assist product managers in identifying and capitalizing on opportunities, and mitigating or avoiding potential threats. For example, if a product manager spots a requested feature which would address a significant weakness in the system, they can implement this as a high priority within the project plan.
3. Set the strategy
Creating a clear product strategy is critical for effective management. By developing a blueprint for your product, you can ensure that everyone on your team is on the same page and understands the vision. Additionally, having a product strategy in place will help you stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked.
To ensure that projects are completed on time, and within budget, it’s vital to understand the product requirements and the target audience. Without a product strategy, it can be challenging to make decisions about project scope and priorities.
A good strategy will consider the competition, the target market, and the company’s strengths and weaknesses. It should also define the key features and benefits of the product. Once the product strategy is finalized, it can be used as a guide for product management.
Managers can use the product strategy to create a project plan that includes a timeline and budget. They can also use it to help them decide which features should be included in the product. The product strategy can create user stories and acceptance criteria.
4. Collect feedback
Feedback refers to evaluating a product, service, or process by its users or customers. It can provide valuable insights to help organizations improve their products and services. Good feedback collection practices involve:
- Identifying who to collect feedback from.
- Designing effective feedback mechanisms.
- Following up on feedback.
Feedback can help organizations make amendments and corrections during a project, or before the launch. It can also be used to improve the long-term strategy. For example, if the feedback collected indicates a demand for a particular product or service, the organization can consider adding that product or service to its portfolio.
When team members provide feedback to one another, it helps to build trust and transparency. This is especially important early on in a project when team members are still getting to know each other. Feedback can also help identify potential issues early on so that they can be addressed before they become more significant problems.
Good feedback collection practices are important for project success whereas inaccurate or incomplete feedback can lead to misguided actions, wasted resources, and unsuccessful projects.
5. Off it goes!
Domain knowledge forms the basis for sound product management. The product manager must track the product development process, marketing activities, and outcomes. In this way, they can use the feedback to improve the product.
The manager’s understanding of the product and the market is critical for determining when a product is ready for launch. For example, if the product manager sees that the marketing budget for the product is low and the reaction to the product is mixed, the manager might advise delaying the launch until more promotable features can be added, or the advertising budget can be increased.
Marketing activities also provide feedback about what users want from a product or feature. By tracking marketing activities, the product manager can understand what features and functions are most important to users and what product areas need the most improvement. Tracking marketing can help the manager ensure that the product meets user needs and expectations while also helping to prevent and solve potential problems.
Ultimately, having an effective and clear process in place as a product manager is necessary for a successful product delivery.
Although product managers don’t have to go through each stage alone… with the seamless integration of tech, software tools can make each process more efficient and agile.
With craft.io, you can easily monitor your project’s progress. You can track the status of each task, document product strategy, and connect it to execution. Utilizing this software is an easy way to ensure you’re on the right track and making the most of your resources and time.